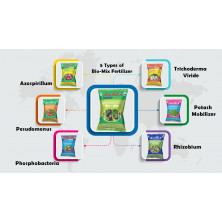
Phosphobacteria means microbial inoculants capable of solubilizing phosphate. Commonly used Phosphobacteria is Bacillus megaterium.
Around 95-99% of the total soil phosphorus is insoluble which is directly not available to plants.
Multiplies fast in the root zone.
The P-solubilizers containing bacteria or fungi may convert isolable form of phosphate to soluble form by producing organic acids in general.
About 15-25% of insoluble phosphate can be solubilized, saving chemical fertilizers significantly.
bacteria, living in close proximity with the root zone.
About 15-25% of insoluble phosphate can be solubilized, saving chemical fertilizers significantly.
Phosphobacteria can solubilize about 30 kg of insoluble source of phosphorus and making it available to plants.
Application of phosphobacteria along with nitrogen fixing bacteria promotes growth and yield of the crops by 30%.